Call 864-261-7474
Today
To schedule an Appointment
Blog Post
Atrial Fibrillation: What You Need to Know
- By Admin
- •
- 08 Oct, 2018
- •
More than 2.7 million people in the U.S. have atrial fibrillation, also known as AF, according to the American Heart Association. This cardiac condition causes irregular heartbeats and may lead to serious situations such as stroke. If you're concerned that you might have AF, take a look at the steps that can lead to a doctor's diagnosis.
Red Flags
What symptoms indicate the possibility of AF? One of the first signs that AF patients have is a fluttering feeling in their chest. Some people who suffer from this cardiac condition can also feel skipped or extra heartbeats.
AF patients may also experience dizziness, weakness, difficulty breathing, or fatigue. While these symptoms are possible in people who don't have atrial fibrillation, they do require further evaluation by a medical professional.
Cardiac Risks
Can anyone have AF? Simply stated, yes. But there are some risk factors that increase your chances of developing this cardiac disease. Age (being over age 80), diabetes, genetics (family history), and existing heart disease all increase your risk, according to the Johns Hopkins University. Along with these factors, obesity may also add to your risk.
In-Office Diagnostic Testing
How will the doctor make an AF diagnosis? Typically, this isn't a one-time-and-you're-done visit. The medical provider will start with a thorough exam and health history. They may ask you questions about your lifestyle, family history of cardiac conditions, chronic conditions, and other health issues. They'll also want to know what happens when you experience cardiac symptoms.
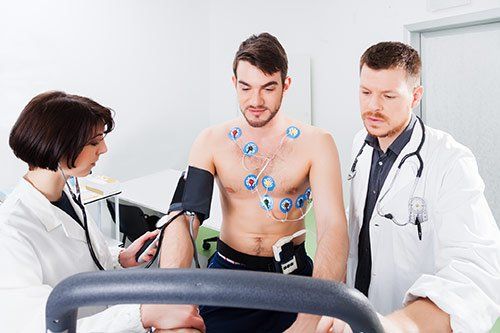
Diagnostic tests, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiogram, are necessary to verify the irregular heartbeat. Both tests are noninvasive, meaning that they do not require surgery. During an ECG, the doctor or technician will place sensors on your chest and arm to monitor your heart's electrical signals.
If you've had an ultrasound, you know the basics behind an echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves (like an ultrasound) to create a video picture of your heart as it works in real time. The echocardiogram allows the doctor to search for a structural abnormality or any other condition that may contribute to heart disease (such as thickening of the heart wall).
At-Home Diagnostic Testing
Some people have AF and still have normal ECGs or echocardiogram. The ECG only picks up electrical changes during the test itself. If you have atrial fibrillation but are not in the middle of an episode, the ECG may show a normal heart rhythm. This makes it more challenging but not impossible for the medical provider to correctly diagnose the condition.
If the doctor suspects that you have AF but your cardiac tests look normal, they may recommend an at-home monitor. A Holter monitor is a portable device that measures and records your heart's rhythm during your normal day. You will wear the monitor for at least 24 hours and engage in your regular activities.
Some patients require further monitoring to catch AF symptoms. If the doctor feels that you do have the condition but doesn't see evidence on the Holter monitor results, they may ask you to wear an event recorder.
You'll wear this portable ECG for weeks or longer. If you feel a flutter, missed heartbeat, fast heartbeat or anything else unusual, you can press a button that allows the device to create a record of (ECG strip) of the event. This provides the doctor with a full picture of what your heart is doing and when.
Post-Diagnosis Care
According to Johns Hopkins University, 35 percent of people diagnosed with this condition will suffer a stroke. Due to the dramatically increased stroke risk, you should get immediate and effective treatment.
Luckily, patients diagnosed with AF have options. These include treatment with anti-arrhythmic drugs or surgical procedures (such as ablation). Even though medications and surgical treatments can reduce the severity of your symptoms, they will not cure the disease. During and following treatment you may have to take a blood thinner to reduce the stroke risk.
Do you need cardiac testing? Contact Anderson
Heart & Vascular, PC,
for more information.
Share
Tweet
Share
Mail
Business Hours:
- Mon - Fri
- -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed
Share
Tweet
Share
Mail
Share
Tweet
Share
Mail
Content, including images, displayed on this website is protected by copyright laws. Downloading, republication, retransmission or reproduction of content on this website is strictly prohibited. Terms of Use
| Privacy Policy